[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] Recently, Tang Yongbing, a researcher at the Functional Thin Film Materials Research Center of the Institute of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his team, together with Professor Li Zhensheng of the City University of Hong Kong, successfully developed high-nitrogen-doped porous microcrystalline carbon nanomaterials. The cathode of the potassium ion battery exhibits high capacity and long cycle characteristics. Related research results "Ultrahigh Nitrogen Doping of Carbon Nanosheets for High Capacity and Long Cycling Potassium Ion Storage" ("High Nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanomaterials with High Capacity and Long Cycle Potassium Storage Performance") published online in the journal Energy Materials Advanced Energy Materials Advanced Energy Materials").
Due to the abundant potassium reserves and the standard hydrogen electrode potential (-2.93 V) close to lithium, potassium-based energy storage devices have good application prospects in the field of large-scale energy storage. However, due to the large ionic radius of the potassium ion (1.38 angstrom), it not only hinders its insertion/extraction in the electrode material, but also has a slow kinetics, which also leads to a large volume change of the electrode material, resulting in a higher cycle stability. difference. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop an efficient and low-cost electrode active material for potassium ion storage.
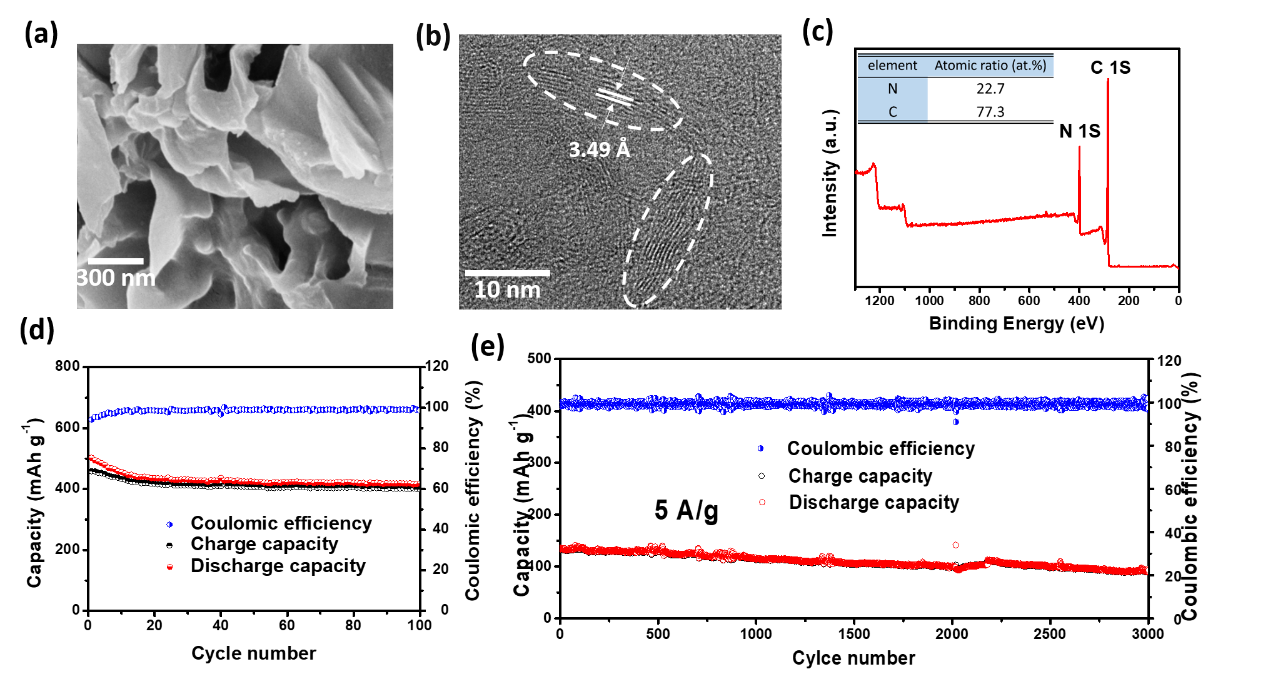
Based on the above considerations, Tang Yongbing and his team members Chang Xingqi, Zhou Xiaolong, Ou Xuewu and others successfully developed high-nitrogen-doped porous microcrystalline carbon nanomaterials, whose porous structure is conducive to the rapid diffusion of potassium ions, and contains a large number of micro Crystal carbon nanosheets facilitate the intercalation and adsorption of potassium ions. The results show that the electrochemical reaction of the high-nitrogen-doped microcrystalline carbon nanomaterials is a synergistic mechanism between the diffusion reaction and the tantalum-capacitance reaction. The potassium-electrode negative electrode has a high capacity of ~410 mAh/g and is 5Ag-1. The capacity retention rate after reversible cycle 3000 times at a large current density is about 70%. This work provides a new strategy for designing high performance potassium anode materials.
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong International Cooperation Project, and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Project.
Jin Yuankang, electroplating, RHODIUM, derived from rhodon, meaning "Rose", because the present solution rhodium salt rose pink color, used for protection and decoration.
Rhodium plating can form a bright and hard coating on the surface of the material. Rhodium itself is more expensive, rhodium Plating Process is a very good jewelry technology, rhodium stability and retention time, are difficult to match the other coating process. Therefore, a strict requirements on the process of the enterprise, will choose to enhance the performance of rhodium plating products, improve product quality.
Rhru Plate,Electroplated Rhodium Ruthenium,Rhodium Ruthenium Products
Jin Yuan Kang Industry Co., Ltd. , http://www.jykplating.com
