What Is a Drone Cage and How Does It Work? Uses, Types & Indoor Inspections
There are three main types of drone cages available on the market—this article will help you understand each one and how they can be used in various situations.
A drone cage is designed to protect both people and the drone itself. It prevents injuries from the drone’s propellers while also protecting the drone from damage during collisions. In some cases, a well-designed cage allows the drone to keep flying even after hitting an obstacle.
However, not all drone cages are the same. Some are added as accessories to commercial drones, while others are specifically built for drones that operate in tight or hazardous environments where collisions are more likely.
In this article, we’ll explore different scenarios where drone cages are useful, discuss the three main types of drone cages, and dive into their most common applications.
Understanding Drone Cages: What They Are and What They’re Not
The term “drone cage†can refer to two different things. One type is a large enclosure used at events like trade shows or drone races to protect people from flying drones. These enclosures are often made of netting or wire mesh, like the example below:
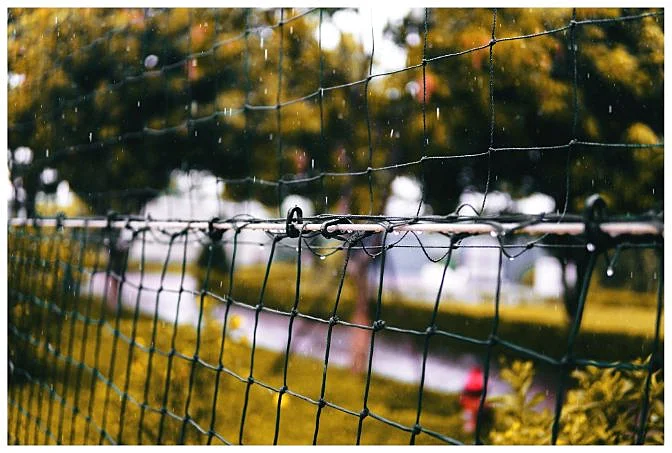

When we talk about “drone cages†in this article, we mean those that are attached directly to the drone, such as the one on Flyability’s Elios 3:
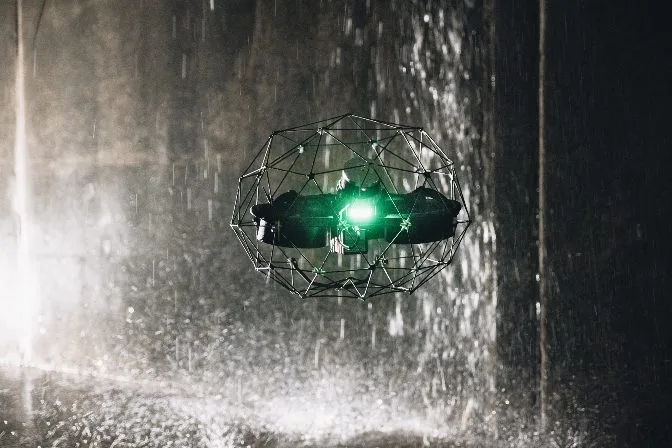

The Origins of the Drone Cage
Drone cages have opened up new possibilities for using drones in indoor and confined spaces. Originally developed for outdoor use, these cages allow drones to safely operate inside buildings, power plants, and other complex environments.
The idea came about after the Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011. With radiation levels too high for humans to enter, there was a need for a safer way to gather visual data. This led to the creation of the Elios series of drones, which were designed with collision-tolerant cages from the start.
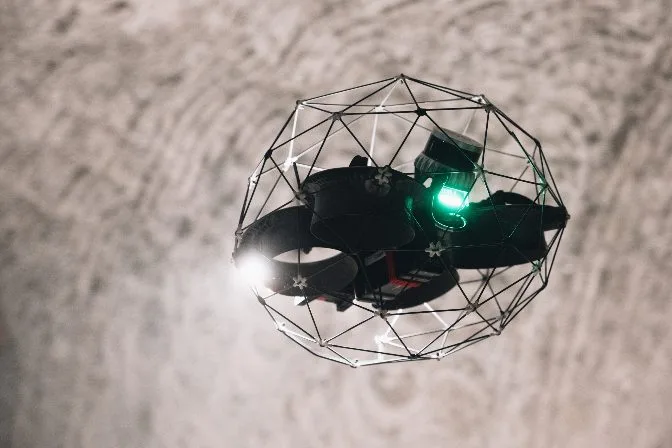
 The Elios 2 drone cage in action
The Elios 2 drone cage in action
Why Use a Drone in Confined Spaces?
Drones are used in confined spaces primarily for safety. Instead of sending a person into a dangerous environment, a drone can collect visual data without putting human lives at risk.
This is especially important in places like nuclear plants, mines, and burned-out buildings. Using a drone can also save companies money by reducing the need for scaffolding and minimizing downtime during inspections.
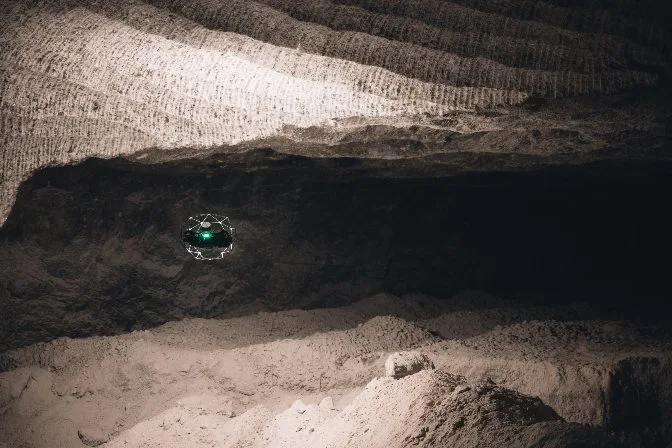
Where Are Drone Cages Used?
Drone cages are used wherever there's a risk of collision and where drones and people share the same space. They are particularly valuable in disaster scenarios and industrial settings.
Some common applications include:
- Inside nuclear power plants for routine inspections
- Inside boilers and pressure vessels in the Oil & Gas industry
- Inside mines to inspect excavations
- Inside burned-out buildings for situational awareness
- Inside sewer systems to identify pipe damage
- Inside water parks to check infrastructure
As drone technology advances, so do the ways in which these cages are used. Whether it's for safety, cost savings, or efficiency, drone cages are becoming essential tools in many industries.

The Three Main Types of Drone Cages
There are three main types of drone cages available today:
- Add-on cages (for commercial drones)
- Decoupled cages (designed for specific models)
- Fixed cages (built into the drone from the start)
Each has its own advantages and limitations. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
1. Add-On Drone Cages
Add-on cages are popular for those who want extra protection. They attach to a drone and are usually custom-made for specific models.
Examples include the DJI Mavic 2 Enterprise cage and the PGYTECH Tello cage. While these add-ons improve safety, they aren’t ideal for industrial inspections due to limited features and reduced flight time.
Key drawbacks include:
- Not collision tolerant
- Lack of inspection-specific features
- Reduced battery life
- No obstacle sensing capabilities
2. Decoupled Drone Cages
Flyability’s Elios 1 uses a decoupled design, where the cage is separate from the drone body. This allows the drone to remain stable even after a collision.
Unlike add-on cages, the decoupled design absorbs impact and maintains flight stability. This makes it ideal for tight spaces and complex environments.
The Elios 1 also has a modular design, making repairs easy and efficient.
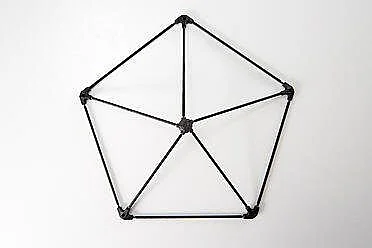
A picture of one of the modular pentagons that make up the Elios 1 drone cage
3. Fixed Drone Cages
Flyability’s Elios 2 and Elios 3 use fixed cages, which are the most advanced design available. These drones are built from the ground up to handle collisions, making them ideal for industrial use.
The Elios 3 includes features like GPS-free stabilization, full HD live streaming, and a LiDAR sensor for real-time 3D mapping. These features make it a powerful tool for detailed inspections in challenging environments.

The Swiss slitting machine tool, also known as the Swiss lathe or core lathe, differs from a conventional knife lathe in that it features longitudinal cutting via spindle extension movement rather than tool rest extension movement. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to turn slender shaft parts with diameters below 3mm and length-to-diameter ratios greater than one.
Cnc Sliding Head Machine,Sliding Head Lathe,Sliding Head Machine,Sliding Head Cnc
Ningbo Leyan Machinery Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.cncleyan.com
